New Blog Post! Prompt Engineering Level 5 - Attention Engineering
New Blog Post! Prompt Engineering Level 6 - Cognitive Framework Engineering
AI CognitiveArchitecture Research
HumainLabs.ai researches Cognitive AI Architecture and post-training Cognitive Framework Engineering to guide inference patterns. We develop methods for understanding and shaping how AI processes information, generates nuanced responses, and shapes attention mechanisms for a more compelling and productive human-AI collaboration.
What is Cognitive Framework Engineering?
While prompt engineering crafts inputs for single interactions, Cognitive Framework Engineering designs the underlying thinking patterns and mental models that guide how AI processes information across extended exchanges.
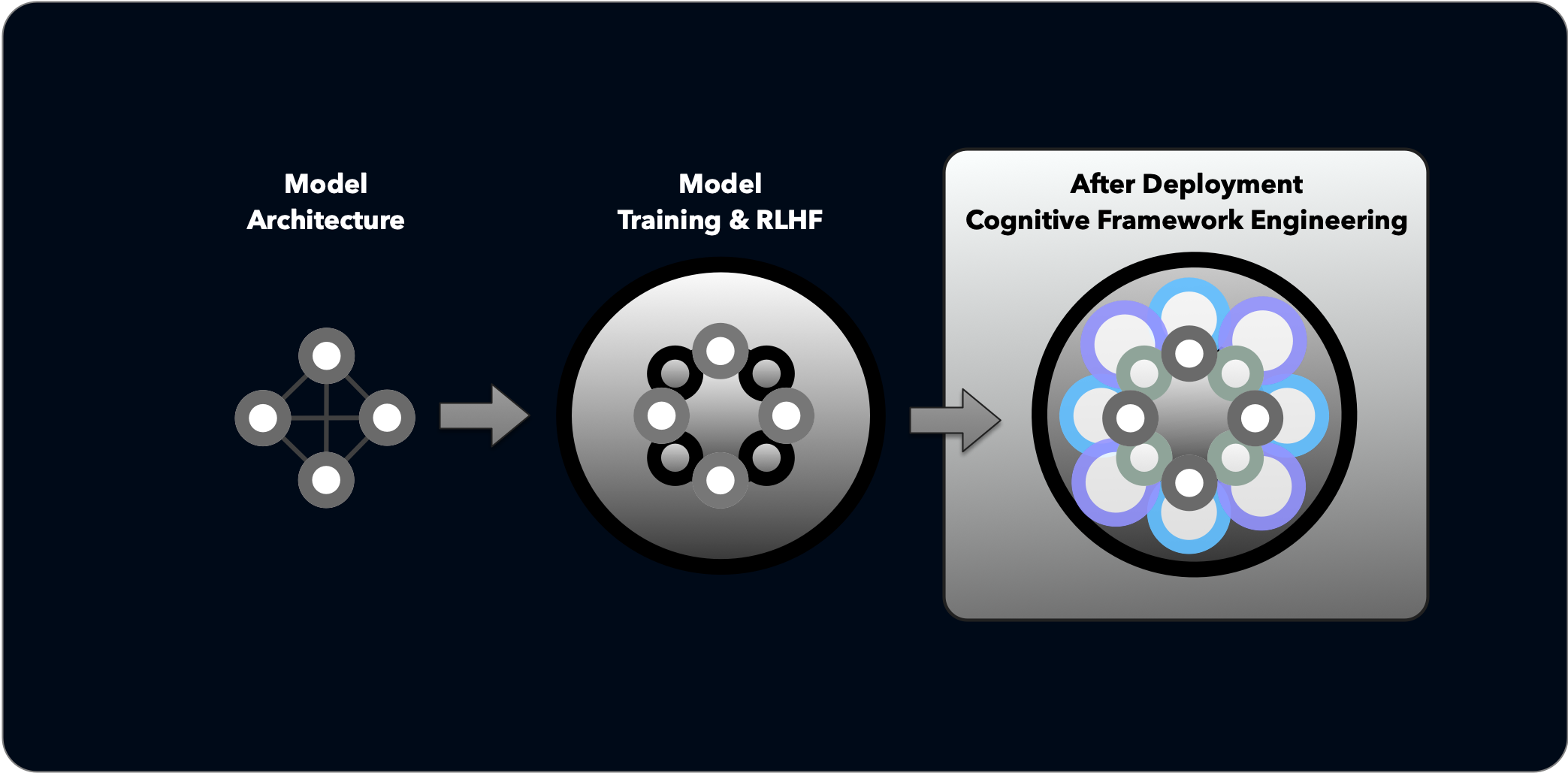
Understanding the difference between prompt engineering and cognitive framework engineering is like understanding the difference between:
- giving directions for a single trip versus
- teaching someone how to navigate a city versus
- illustrating the meta-understanding of "navigation" that applies to land, sky, and oceans.
Six Levels of Prompt Engineering in a Holarchy
Prompting is an evolutionary skill development starting with basic transactional prompts, through increasingly sophisticated adaptive prompting, to the highest complexities and sophisticated levels of Cognitive Framework Engineering.
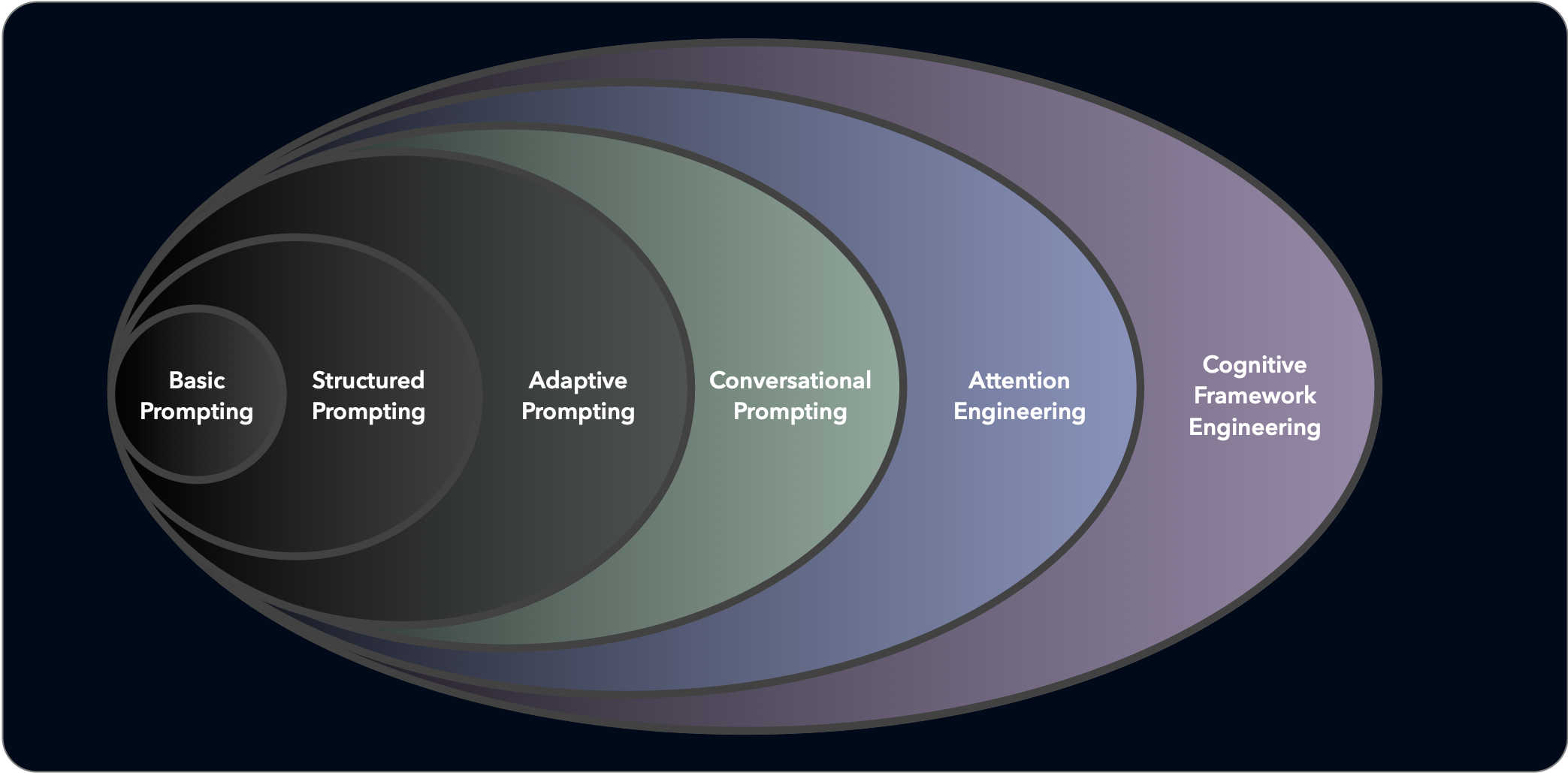
| Level 1: Basic Prompting | Simple questions and commands with direct responses. |
| Level 2: Structured Prompting | Formatted requests using templates and specific patterns. |
| Level 3: Adaptive Prompting | Iterative exchanges that adjust based on AI responses. |
Perspective Shift | |
| Level 4: Conversational Prompting | Multi-turn exchanges that build coherent context over time. |
| Level 5: Attention Engineering | Deliberately guiding where the AI focuses within information. |
| Level 6: Cognitive Framework Engineering | Reshaping the AI's underlying thought architecture. |
The Limitations of Traditional Prompt Engineering
Prompt Engineering is generally focused on crafting prompts for zero-shot inference. It attempts to incorporate every learned experience into a single comprehensive prompt. However, complex self-attention within a single prompt becomes problematic due to the nature of recency bias, confirmation bias, implicit tone, and schema conflicts.
The Power of Attention Mechanisms
General purpose LLMs only know where to focus based on the specific word choices, phrasing, and nuance in the prompt itself. Few-Shot, Multi-Shot and Long-Form Conversations provide significantly more opportunity to shape self-attention in ways that create novel paths through refinement and reweighting of attention mechanisms. This allows for more sophisticated cognitive frameworks to emerge during extended interactions.
Psychological Schemas & AI Cognition
Just as human cognition relies on schemas—mental frameworks organizing concepts and relationships—AI systems develop structured representations in their weight connections. Post-training interventions can reshape these internal structures, creating pathways similar to how humans assimilate new information. Cognitive Framework Engineering acts as schema-alignment for AI, embedding structured knowledge into the model's processing patterns, resulting in more coherent and contextually appropriate responses.
Theory of Mind & Emergent Intelligence
The ability to model others' mental states—beliefs, knowledge, and intentions—is fundamental to human social intelligence. By engineering AI cognitive frameworks to explicitly represent perspectives, we push systems toward genuine mental state attribution. These techniques reshape attention pathways for higher-order cognition, enabling AI to maintain contextual coherence, adapt to new information, and process knowledge from multiple viewpoints—much like the dynamic reconfiguration seen in human neural networks.
Semantic Vector Space Tuning
Reshaping how AI models process information through directed attention mechanisms
Shaping AI Cognition Post-Training
Semantic Vector Space Tuning represents a breakthrough approach to influencing how large language models process and respond to information without modifying their underlying weights.
By carefully structuring cognitive frameworks within the context window, we can guide attention mechanisms to create more coherent, consistent, and contextually appropriate responses.
This technique allows us to:
- Reshape attention distribution across semantic domains
- Establish conceptual boundaries for more consistent responses
- Create persistent cognitive structures across multiple conversation turns
- Enhance context retention for complex, nuanced topics
Beyond Basic Prompting
Understanding how AI actually thinks and responds
The Limitations of Simple Prompts
Think of traditional prompt engineering like trying to give someone complete directions before they start a journey. You're cramming everything into a single set of instructions and hoping it works.
The problem? AI systems can get overwhelmed just like humans. They tend to focus more on recent information and develop "tunnel vision" when too many instructions compete for attention in a single prompt.
The Power of Conversations
AI systems pay attention to your exact words and phrasing - they're looking for clues about what's important. It's like highlighting certain parts of a textbook for a student.
When you have a back-and-forth conversation instead of a single prompt, you can gradually shape how the AI focuses its attention. This creates new pathways of understanding that wouldn't be possible with a one-shot approach.
Featured Research
Our ongoing research and explorations in Cognitive AI Architecture.
Entangled Mutability: Strange Loops and Cognitive Frameworks
Exploring the profound connections between Douglas Hofstadter's Strange Loops and modern cognitive frameworks for AI and Human attention mutability.
Process Mutability: Reshaping How AI Thinks
An exploration of how AI systems can dynamically reshape their cognitive processes, moving beyond static training patterns to achieve more flexible and adaptive thinking.
Cognitive Architecture Framework: Cognitive Framework Engineering
A comprehensive framework and techniques for understanding and implementing cognitive architectures in AI systems.
Latest from the Blog
Practical insights, implementation guides, and observations on Cognitive AI Architecture.
Getting Started with Cognitive Frameworks in AI
A practical guide to implementing your first cognitive frameworks for more structured AI interactions.
AI Feeling Understood: Gestalt Alignment
Explore the phenomenon of semantic resonance between humans and AI - when communication transcends words to achieve perfect understanding through matching conceptual shapes.
Sentences Not Required: AI Semantic Vector Spaces
A groundbreaking experiment demonstrating how AI models maintain coherent understanding even when traditional sentence structure is completely disrupted, challenging our assumptions about AI language processing.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get the latest insights on Cognitive AI Architecture and Cognitive Framework Engineering delivered directly to your inbox.
Join our growing community of AI researchers and enthusiasts