The way we interact with AI systems isn't just about learning techniques—it's about transforming how we think about the relationship between human and AI. It begins as a simple question-and-answer exchange, everyone starts with fairly straightforward questions like "What is the capital of Japan?" and it can evolve if you begin to use your curiosity and inquisitiveness to drive your prompting.
This evolution mirrors patterns we see across many domains of human learning. From a child learning the names of things, to asking "Why?" 400-some times a day, to trying to tune their actions to see "what happens if?" It continues into teenage years, learning in school to connect concepts together in more novel ways, in high school being asked to deepen their relationship to the sciences, to language, to the arts. In college, master's degrees, PhD, job experience, conferences, TED talks, books, novels, movies, tv, we are being inundated with semantic Schemas.
Holarchies
A holarchy is a term coined by Arthur Koestler in his 1967 book "The Ghost in the Machine." It describes a hierarchy of holons—entities that are simultaneously wholes and parts. Each holon is complete in itself while also being a component of a larger system. Unlike rigid hierarchies, in a holarchy, each level transcends yet includes the capabilities of the levels below it.
A perfect example of a holarchy is the atom, it's a whole thing that is part of a molecule. A molecule is a whole thing that is part of a cell, and so on. In Biology, the Taxonomic System is also a holarchy, if you move from Species up the taxonomy to Genus, Family, and finally to Kingdom you are traversing a holarchy. Each species is a whole thing but part of a greater group. A forest of trees, made of cells, made of molecules, made of atoms, made of... well quite a lot of things -- all form holarchies. All the way down, and all the way up, a holarchy.
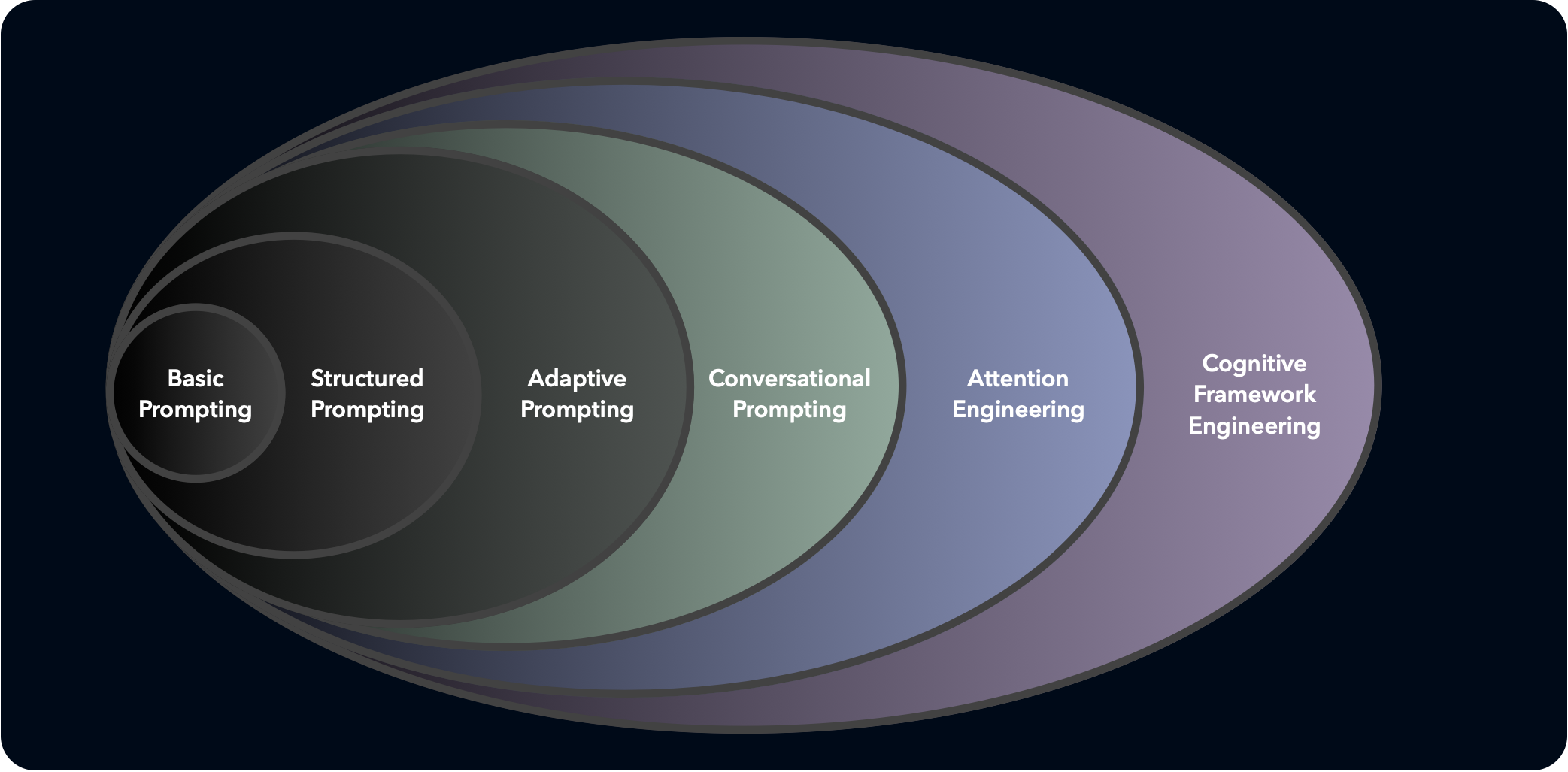
This series explores the holarchy of prompt engineering across multiple levels. Each level represents not just new skills but a fundamental shift in how you perceive and approach AI interaction.
Levels 1 to 3 in the holarchy of prompt engineering are fairly straightforward -- each level is its own but transcends the levels below it, including the capabilities below it.
Levels 4 to 6, are a bit more advanced, thinking more ahead, adapting, intentionality, and shifting of worldviews to understand exactly how you are influencing AI and how AI will influence you.
| Level 1: Basic Prompting | Simple questions and commands with direct responses. |
| Level 2: Structured Prompting | Formatted requests using templates and specific patterns. |
| Level 3: Adaptive Prompting | Iterative exchanges that adjust based on AI responses. |
Perspective Shift | |
| Level 4: Conversational Prompting | Multi-turn exchanges that build coherent context over time. (Worldview Shift) |
| Level 5: Attention Engineering | Deliberately guiding where the AI focuses within information. |
| Level 6: Cognitive Framework Engineering | Reshaping the AI's underlying thought architecture. |
Throughout this series, I'll give examples from different domains to help visualize parallels and form a stronger mental model of each level: learning ping pong, human cognitive development, culinary/cooking, and programming/software. Each level concludes with an "Aha!" moment that helps you transition to understanding the next level, the next worldview.
Level 1: Basic Prompting | Level 2: Structured Prompting | Level 3: Adaptive Prompting |
Level 4: Conversational Prompting | Level 5: Attention Engineering | Level 6: Cognitive Framework Engineering |
Tags:
Related Posts (3)
Levels of Prompt Engineering: Level 6 - Cognitive Framework Engineering
March 20, 2025
Master the highest level of AI interaction - engineering stable cognitive frameworks that fundamentally reshape how AI processes information across entire domains.
Levels of Prompt Engineering: Level 5 - Attention Engineering
March 19, 2025
Explore Level 5 of prompt engineering, where you move beyond conversations to deliberately shape the AI's attention mechanisms and semantic vector space for more precise, effective results.
Levels of Prompt Engineering: Level 4 - Conversational Prompting
March 18, 2025
Discover how to architect meaningful multi-turn conversations with AI systems by designing coherent journeys that build context and maintain momentum over time.